Multiple pregnancies
- Ultrasound cycle monitoring is mandatory with every ovulation induction and insemination to see how many eggs are maturing. In the case of multiple follicular maturation we can cancel the cycle or we can aspirate the supernummarary oöcytes
- In IVF or ICSI we have complete control on the number of embryo’s that are transferred to the uterus. This reduces the chances of multiples gestation. Cave! Monozygotic twins do occur also after IVF or ICSI. Maybe the risk is even slightly higher.
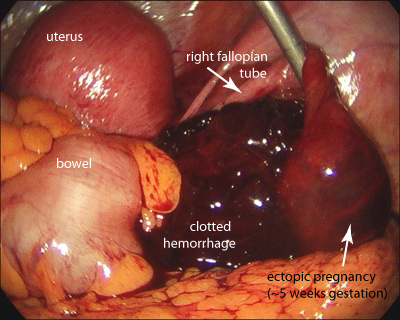
Extrauterine pregnancies and miscarriages.
Just like with a natural pregnancy, EUP and miscarriage is also possible after fertility treatments. The risk may also be slightly elevated. You will be followed closely once a pregnancy is diagnosed with the first blood check. A second blood check is done after one week and a first ultrasound will follow in the weeks thereafter. You will be referred to your own gynaecologist for the follow up of your pregnancy.
Side effects of hormonal treatments
- Clomid: this antioestrogen has specific side-effects in a minority of women. Sometimes they are severe like hot flushes, head-ache, bloating and nausea, mood swings, visual disturbances
- Menopur and other gonadotrophins have no direct side effects. Their side effect are related to the effects they have on the ovaries like the maturation of multiple follicles who produce suprafysiological amounts of estrogens. This can accentuate cycle related side effects such as: nausea, breast tenderness, bloating etc..
Specific for insemination
- Bleeding after insemnation may be procedure related and is normal. It will diminish after one day.
- Infection after insemination is very uncommon. The semen sample is washed carefully in a sterile environment. Most bacteria are eliminated.
Specific for IVF and ICSI
- Bleeding: During the aspiration of oöctes a needle is introduced in the ovary through the vaginal wall. After the prcedure the vagina can bleed a little. This is diagnosed immediately and easely dealt with. Also the ovary can bleed a little. This can cause some disconfort after the procdure. In less than 1/1000 this bleeding is exaggerated and needs to be dealt with during a laparoscopic intervention
- Infection: the vagina is a non sterile environment. A transvaginal punction has a certain risk of transmitting bacteria and causing infection. We see less than 1% of infections after oöcyte aspiration. Certain risk population receive profylactic antibiotics
- Perforation: we try to avoid transvesical puncture aldough it may sometimes be necessary. In this case you are advised to drink abundantly, you will receive an antibiotic and sometimes a bladdercatheter is installed. Punctures through intestines are allways avoided. Accidental puncture is allways treated with antibiotics